Chat
Initialization & Imports
from waii_sdk_py import WAII
from waii_sdk_py.chat import *
from waii_sdk_py.query import *
from waii_sdk_py.database import *
from waii_sdk_py.semantic_context import *
from waii_sdk_py.chart import *
from waii_sdk_py.history import *
WAII.initialize(url="https://your-waii-instance/api/", api_key="your-api-key")
The Chat module contains methods to interact with a SQL Chatbot.
Important: You need to activate the database connection first before using the methods in this module. Otherwise, you may be conversing with the wrong database.
WAII.Database.activate_connection("snowflake://...&warehouse=COMPUTE_WH")
Here are some of its methods:
Send Chat Message
WAII.Chat.chat_message(params: ChatRequest) -> ChatResponse
This method sends a message to the chatbot based on the provided parameters.
ask: The question you want to ask the chatbot regarding your databaseHow many tables are there?parent_uuid: The uuid of the previous chat message if you want to continue the conversationuse_cache: Whether to use cache or not, default is True. If you set it to False, it will always generate a new query by calling LLM.model: Which LLM to be used to generate queries. By default system will choose a model.modules: List of components to generate (Query, Data, Chart, Tables, Context). Default: all of them.chart_type: Currently waii supports vegalite, superset and metabaseadditional_context: (optional) List ofSemanticStatementobjects to provide additional context during chat. These context will be treated like they are part of the system and follow all fields of the context. See Semantic Context module for detailed information aboutSemanticStatementfields and usage patterns.mode: The chat mode to use. Options are:ChatRequestMode.single_turn(default): Standard single question-answer interactionChatRequestMode.multi_turn: Enhanced multi-turn conversation with clarification and follow-up capabilitiesChatRequestMode.deep_research: Advanced research mode for complex analytical queriesChatRequestMode.automatic: System automatically chooses the best mode
The ChatResponse contains different objects that represent the answer to the question
response: A templated response representing the answer to the question. The values for the templates can be found in the chat_response_data. The possible templates will be listed in the template sectionchat_uuid: The uuid of the message, use this uuid as the parent uuid to continue the conversationis_new: If sql was generated to answer this question, this field is true if the sql has been identified as a new query, not a tweak of the previous query that was maintained during the conversationtimestamp_ms: The timestamp of the chat responseelapsed_time_ms: Time elapsed for the chat response generationsession_title: Optional title for the chat sessionresponse_data: AChatResponseDataorChatResponseDataV2object containing the generated info for the question. AChatResponseDataobject looks likesemantic_context: AGetSemanticContextResponseobject containing the semantic context from the database related to the ask and generated querytables: ACatalogDefinitionobject containing the related tables to the questioncatalog: ACatalogDefinitionobject containing the related tables to the question, if createdsql: AGeneratedQueryobject containing the generated query to answer the question, if createddata: AGetQueryResultResponseobject containing the result of the generated query if it was runchart_spec: AChartGenerationResponseobject containing the information for the visualization
status_update_events: List ofChatStatusUpdateEventobjects providing real-time status updates during processing
Examples:
Ask a new question:
>>> response = WAII.Chat.chat_message(ChatRequest(ask = "How many tables are there?"))
Use multi-turn mode for enhanced conversation:
>>> response = WAII.Chat.chat_message(ChatRequest(ask = "Analyze our sales performance",
mode=ChatRequestMode.multi_turn))
Restrict response components (only get SQL):
>>> response = WAII.Chat.chat_message(ChatRequest(ask = "Revenue by year",
modules=[ChatModule.QUERY]))
Ask a follow-up question:
>>> response = WAII.Chat.chat_message(ChatRequest(ask = "tables with more than 100 rows?",
parent_uuid=response.chat_uuid))
Response Templates
Template names will be enclosed in {}, such as {tables}
tablesThe database tables that were used to generate the results (just a list of the names)sqlThe query generated to answer the question from the databasedataThe data generated by running the querystepsA step-by-step explanation in English of how results were computed from the databasecompilation_errorsThe compilation errors for the generated sql detected by our SQL compilergraphA graphical representation of the data from the database
Async Chat Message Generation
The generate_chat() endpoint carries out the chat message generation synchronously. This will block until Waii generates a valid chat response. To generate a chat message asynchronously, use the following pair of methods:
WAII.chat.submit_chat_message(params: ChatRequest) -> AsyncObjectResponse
WAII.chat.get_chat_response(params: GetObjectRequest) -> ChatResponse
The AsyncObjectResponse and GetObjectRequest both contain a single field:
uuid: A unique identifier for the chat message generation request.
Both submit_chat_message and get_chat_response are non-blocking calls. submit_chat_message will immediately return with the uuid, and get_chat_response will return the intermediate generated chat response. The ChatRequest and ChatResponse follow the same semantics as above.
ChatResponse includes an additional field called current_step of type ChatResponseStep, which is relevant during async chat message generation. This is updated as the message is generated, along with other fields of the chat response as they are determined. None of these fields are considered finalized until the current_step becomes Completed.
Response Selection
The response_selected_fields property indicates which modules ultimately contributed to the final response based on the requested modules and module_limit_in_response parameters.
ChatResponseStep values:
- Routing Request
- Generating Query
- Retrieving Context
- Retrieving Tables
- Running Query
- Generating Chart
- Preparing Result
- Completed
request = ChatRequest(ask="How many tables are there?")
response = WAII.chat.submit_chat_message(request)
get_chat_response_request = GetObjectRequest(uuid=response.uuid)
generated_chat_response = None
while True:
time.sleep(1)
generated_chat_response = WAII.chat.get_chat_response(get_chat_response_request)
if generated_chat_response.current_step == ChatResponseStep.completed:
break
# analyze intermediate chat response here
# analyze the completed chat response here
Research Template Management
The Chat module provides methods to manage research templates that can be used to standardize and reuse common research patterns.
Create Research Template
WAII.Chat.create_research_template(params: CreateResearchTemplateRequest) -> CommonResponse
This method creates a new research template.
Parameters:
research_template: AResearchTemplateobject containing:title: The title of the templatetemplate: The template content/patterntemplate_id: Optional ID (auto-generated if not provided)
Example:
template = ResearchTemplate(
title="Sales Analysis Template",
template="Analyze sales performance by region and time period"
)
request = CreateResearchTemplateRequest(research_template=template)
response = WAII.Chat.create_research_template(request)
Get Research Template
WAII.Chat.get_research_template(params: GetResearchTemplateRequest) -> GetResearchTemplateResponse
This method retrieves a specific research template by ID.
Parameters:
template_id: The ID of the template to retrieve
Response:
research_template: The requestedResearchTemplateobject orNoneif not found
Example:
request = GetResearchTemplateRequest(template_id="template_123")
response = WAII.Chat.get_research_template(request)
print(f"Template: {response.research_template.title}")
List Research Templates
WAII.Chat.list_research_templates(params: ListResearchTemplatesRequest) -> ListResearchTemplatesResponse
This method retrieves a list of available research templates.
Parameters:
limit: Optional limit on the number of templates to return (default: 10)search_text: Optional search text to filter templates (will use for similarity search through embedding match, not a direct text match)
Response:
research_templates: List ofResearchTemplateobjects
Example:
request = ListResearchTemplatesRequest(limit=20, search_text="sales")
response = WAII.Chat.list_research_templates(request)
for template in response.research_templates:
print(f"- {template.title}: {template.template}")
Update Research Template
WAII.Chat.update_research_template(params: UpdateResearchTemplateRequest) -> CommonResponse
This method updates an existing research template.
Parameters:
research_template: AResearchTemplateobject with the updated information (must includetemplate_id)
Example:
template = ResearchTemplate(
template_id="template_123",
title="Updated Sales Analysis Template",
template="Enhanced sales performance analysis with additional metrics"
)
request = UpdateResearchTemplateRequest(research_template=template)
response = WAII.Chat.update_research_template(request)
Delete Research Template
WAII.Chat.delete_research_template(params: DeleteResearchTemplateRequest) -> CommonResponse
This method deletes a research template.
Parameters:
template_id: The ID of the template to delete
Example:
request = DeleteResearchTemplateRequest(template_id="template_123")
response = WAII.Chat.delete_research_template(request)
Module Configuration Tips
- Use
modulesto limit response generation for faster responses - Start with
[ChatModule.QUERY]for simple SQL generation - Add
ChatModule.DATAandChatModule.CHARTfor full analysis - Use
module_limit_in_response=1to get only the most relevant component - Combine with
chart_typefor specific visualization formats
Supported Chart Types:
Currently waii supports vegalite, superset and metabase
Vegalite Chart
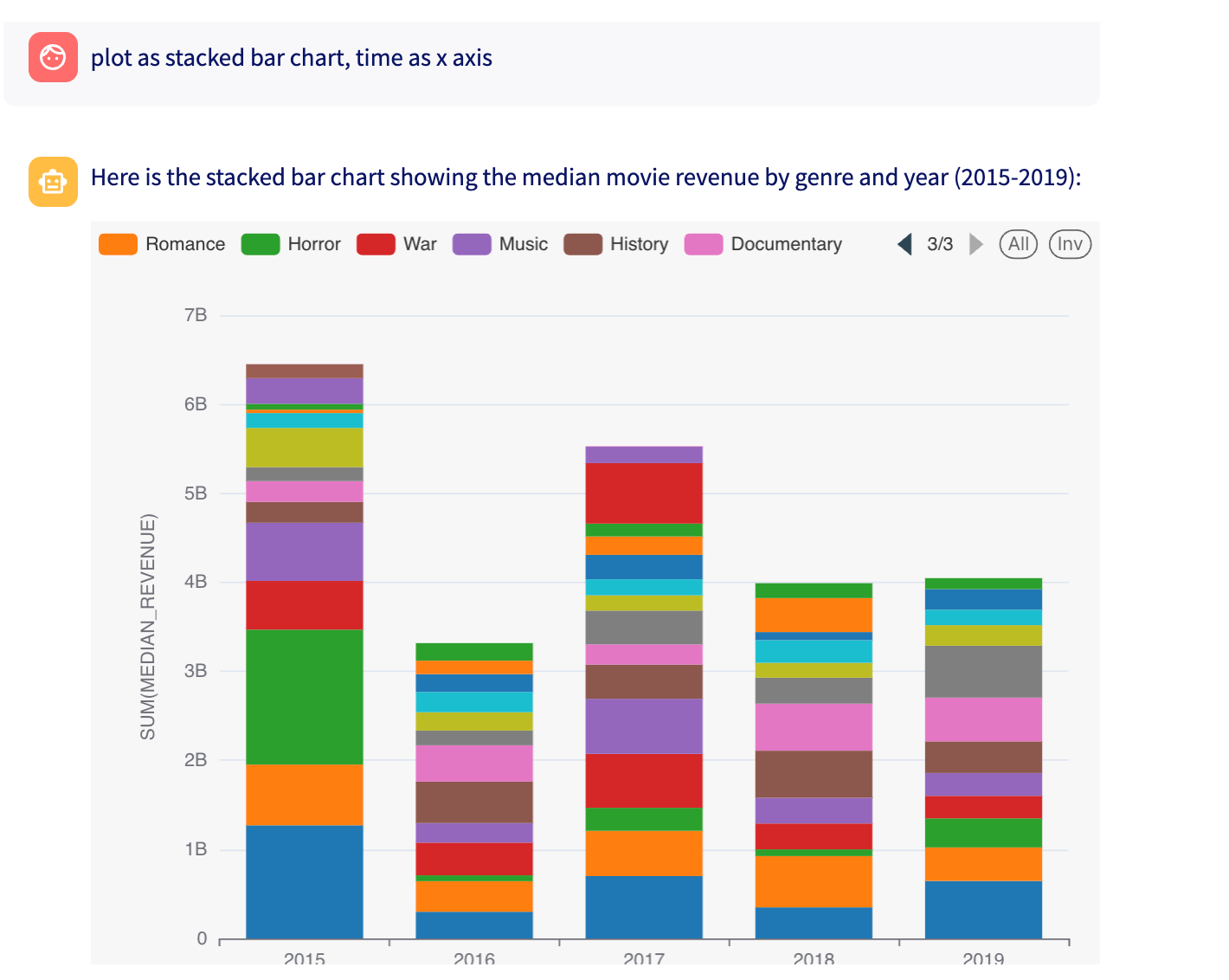
Request:
response = WAII.Chat.chat_message(ChatRequest(ask="Draw a bar graph showing revenue per year", chart_type = ChartType.VEGALITE ))
Response:
{
"response": "Here is a bar graph showing the total revenue per year for movies released after 1980: \n\n<chart>",
"response_data": {
"data": {
"rows": [
{
"START_YEAR": 1981,
"TOTAL_REVENUE": 195312802
},
{
"START_YEAR": 1982,
"TOTAL_REVENUE": 439506293
}
],
"more_rows": 0,
"column_definitions": [
{
"name": "START_YEAR",
"type": "FIXED"
},
{
"name": "TOTAL_REVENUE",
"type": "FIXED"
}
],
"query_uuid": "beef22fc-0a96-4688-bf4f-9c53df55f72c"
},
"query": {
"query": "SELECT\n start_year,\n SUM(revenue) AS total_revenue\nFROM movie_db.movies_and_tv.movies\nWHERE\n start_year > 1980\nGROUP BY\n start_year\nORDER BY\n start_year\n"
},
"chart": {
"uuid": "0b86e535-2e20-42ad-ba0f-95f56f6cf1a5",
"chart_spec": {
"spec_type": "vegalite",
"chart": "{\"$schema\":\"https://vega.github.io/schema/vega-lite/v5.json\",\"data\":{\"url\":\"waii_data.json\"},\"mark\":\"bar\",\"encoding\":{\"x\":{\"field\":\"START_YEAR\",\"type\":\"ordinal\",\"axis\":{\"title\":\"Start Year\",\"labelAngle\":45}},\"y\":{\"field\":\"TOTAL_REVENUE\",\"type\":\"quantitative\",\"axis\":{\"title\":\"Total Revenue\",\"grid\":true}}},\"tooltip\":[{\"field\":\"START_YEAR\",\"type\":\"ordinal\",\"title\":\"Year\"},{\"field\":\"TOTAL_REVENUE\",\"type\":\"quantitative\",\"title\":\"Revenue\"}]}"
}
}
}
}
You can get the vegalite chart specs using
response.response_data.chart.chart_spec
for the above example the chart spec are as follows:
{
"$schema": "https://vega.github.io/schema/vega-lite/v5.json",
"data": {
"url": "waii_data.json"
},
"mark": "bar",
"encoding": {
"x": {
"field": "START_YEAR",
"type": "ordinal",
"axis": {
"title": "Start Year",
"labelAngle": 45
}
},
"y": {
"field": "TOTAL_REVENUE",
"type": "quantitative",
"axis": {
"title": "Total Revenue",
"grid": true
}
}
},
"tooltip": [
{
"field": "START_YEAR",
"type": "ordinal",
"title": "Year"
},
{
"field": "TOTAL_REVENUE",
"type": "quantitative",
"title": "Revenue"
}
]
}
You would need to replace data in the above to view the actual chart i.e.,
response.response_data.chart.chart_spec.data = {
"values":
response.response_data.data.rows
}
Actual chart:
Open the Chart in the Vega Editor
Superset Chart
Request:
response = WAII.Chat.chat_message(ChatRequest(ask="Draw a bar graph showing revenue per year", chart_type = ChartType.SUPERSET ))
Response:
{
"response_data": {
"data": {
"rows": [
{
"START_YEAR": 2015,
"TOTAL_REVENUE": 11987590461
},
{
"START_YEAR": 2016,
"TOTAL_REVENUE": 8735916896
}
],
"more_rows": 0,
"column_definitions": [
{
"name": "START_YEAR",
"type": "FIXED"
},
{
"name": "TOTAL_REVENUE",
"type": "FIXED"
}
],
"query_uuid": "14b6f72e-7379-4a34-8d57-661a2b6f8964"
},
"query": {
"query": "SELECT\n start_year,\n SUM(revenue) AS total_revenue\nFROM movie_db.movies_and_tv.movies\nGROUP BY\n start_year\nORDER BY\n start_year\n"
},
"chart": {
"uuid": "489ab1f2-f4e2-4bd3-9e66-b758e97451cb",
"chart_spec": {
"spec_type": "superset",
"generation_message": null,
"chart_title": "Total Revenue Per Year",
"superset_specs": {
"datasource": "",
"viz_type": "echarts_timeseries_bar",
"y_axis_title_margin": 40,
"color_scheme": "d3Category10",
"x_axis": "START_YEAR",
"metrics": [
{
"expressionType": "SQL",
"sqlExpression": "SUM(TOTAL_REVENUE)",
"label": "SUM(TOTAL_REVENUE)"
}
],
"y_axis_title": "SUM(TOTAL_REVENUE)"
}
}
}
}
}
To create chart in superset, you would need to first create dataset in superset using /api/v1/dataset/ api
Here's simple script:
dataset = self.client.post(f"{self.client.host}/api/v1/dataset/", json={
"database": database_id,
"sql": sql_query,
"table_name": dataset_name,
"normalize_columns": True
})
you can get the sql_query from
response.response_data.query.query
After creating dataset you can pass these specs to /api/v1/explore/permalink
Note: You would need to replace "datasource": "", with the dataset id you get in previous step
Here's simple script to do that:
superset_specs["datasource"] = f"{dataset_id}__table"
permlink_payload = {
"formData": superset_specs
}
permlink = self.client.post(f"{self.client.host}/api/v1/explore/permalink", json=permlink_payload)
permlink will have the superset url which you can embed in your application.
Complete link on how to generate superset iframe
Here's an example chart:
superset chart embedded in streamlit app:
Metabase Chart
Request:
response = WAII.Chat.chat_message(ChatRequest(ask="Draw a bar graph showing revenue per year", chart_type = ChartType.METABASE ))
Response:
{
"response_data": {
"data": {
"rows": [
{
"START_YEAR": 2015,
"TOTAL_REVENUE": 11987590461
},
{
"START_YEAR": 2016,
"TOTAL_REVENUE": 8735916896
}
],
"more_rows": 0,
"column_definitions": [
{
"name": "START_YEAR",
"type": "FIXED"
},
{
"name": "TOTAL_REVENUE",
"type": "FIXED"
}
],
"query_uuid": "14b6f72e-7379-4a34-8d57-661a2b6f8964"
},
"query": {
"query": "SELECT\n start_year,\n SUM(revenue) AS total_revenue\nFROM movie_db.movies_and_tv.movies\nGROUP BY\n start_year\nORDER BY\n start_year\n"
},
"chart": {
"uuid": "489ab1f2-f4e2-4bd3-9e66-b758e97451cb",
"chart_spec": {
"spec_type": "metabase",
"plot_type": "bar",
"dimension": "START_YEAR",
"name": "Total Revenue Per Year",
"color_hex": "#349301",
"metric": "TOTAL_REVENUE"
}
}
}
}
Inorder to add the metabase charts to your app, you can use this script here as reference
Example metabase chart:

Output Templates
Response templates use placeholders to dynamically insert generated content. Available parameters:
\{tables\}: List of relevant table names (e.g.: "movies, actors, genres")\{sql\}: Generated SQL query with syntax highlighting\{data\}: Tabular query results\{steps\}: Step-by-step explanation of query logic (this is from GeneratedQuery.detailed_steps)\{graph\}: Visualization spec or embedded chart (this is chart_spec from the response)
Template Rules:
- Include
\{graph\}when visualization adds value - Use
\{data\}for tabular results (>3 rows) - Show
\{steps\}/\{tables\}/\{sql\}only when explaining methodology (when user explicitly asks for it) - Combine parameters naturally based on question context
Examples:
User question: "Show me total sales last month"
Last month's total sales were \{data[0].total_sales\}
User question: "Visualize revenue trends by year"
Here's the revenue trend by year:
\{graph\}
Generated with:
\{sql\}
User question: "Which tables store customer information?"
Customer data is stored in these tables:
\{tables\}
Sample schema from \{tables[0]\}:
\{context\}
User question: "Why did this query return no results?"
No records found matching your criteria:
\{sql\}
Potential reasons:
1. Filters may be too restrictive
2. Tables might need updating
User question: "Explain how you calculated average order value"
\{steps\}
Here's the SQL query used:
\{sql\}
Final calculation:
\{data\}
User question: "Show top products (raw data) and create pie chart"
Top selling products this quarter:
\{data\}
\{graph\}
** Other notes for response templates:**
- It only use the corresponding template if the generated response contains it (e.g. if the response doesn't contain any visualization, it won't use the {graph} template)
- By default it optimize for the best display of the data, e.g. if the data is better displayed in a table, it will use the {data} template, otherwise, it will use the {graph} template
- If there's any error occured (e.g. user asked for query, but the query generation or run failed), it will synthesize the error message and show it to the user.
- When there're limited data, it can synthesize the data directly to the user instead of showing the raw data (e.g. "Median age for the active users is 30.0")