Single Node Deployment
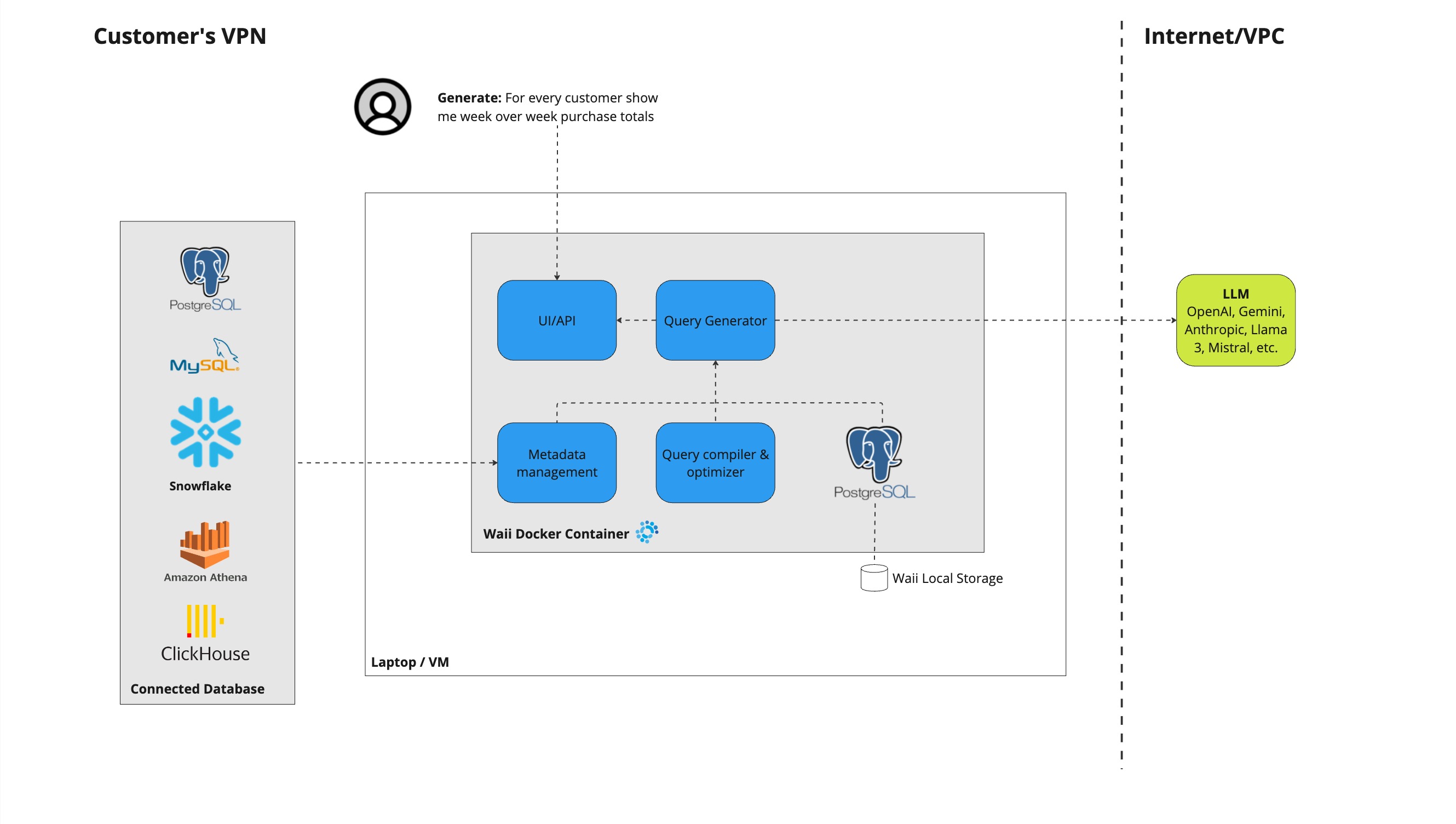
The single node deployment of Waii operates within a Docker container, which can be executed on your laptop or a virtual machine. This container comprises several components:
- UI/API Service: Hosts both UI and API endpoints.
- Metadata Management Service: Retrieves information from your databases and stores it in a built-in PostgreSQL database.
- Query Generator: Utilizes the stored information to produce SQL queries. These queries are generated by the LLM model using the stored information and subsequently refined by Waii's query compiler/optimizer to produce the final query.
- Postgres Database: Maintains metadata and a history of queries.
Network Requirements: The deployment does not require access to Waii SaaS but needs connectivity to LLM model endpoints, such as those provided by OpenAI, other LLM public services, or internal deployments. Depends on where the LLM model is hosted, it can be either Internet (for example OpenAI) or within the same VPC (for example Bedrock or Azure OpenAI).
The subsequent sections will guide you through setting up a single-node Waii instance on Docker and integrating it with your database.
Prerequisites
- Install Docker: Download and install Docker from here, if it's not already installed.
- System Requirements: Ensure your host machine has at least 8GB of available memory. For cloud deployments, an AWS c6a.xlarge instance or equivalent is sufficient for most use cases.
- LLM Configuration: Configure your preferred LLM provider. See Configuring LLM Providers for detailed setup instructions.
Step-by-Step Installation Guide
Authenticate with Docker Hub
Execute the command below in your terminal to log in to Docker Hub. Use the credentials provided separately:
docker login --username waiilabs --password <provided separately>
Pull the waii Docker image
To download the latest version of the sandbox image from Docker Hub, use the following command:
# please replace `<tag>` with the tag you want to use with instruction from Waii team
docker pull waiilabs/sandbox-new:`<tag>`
Run the waii container
First let's setup the directories:
cd ~
mkdir waii-sandbox-test
mkdir waii-sandbox-test/pg
chmod 0700 waii-sandbox-test/pg
mkdir waii-sandbox-test/log
Set tag for docker image (x86_64):
tag="waiilabs/sandbox:latest"
Or, set tag for docker image (aarch64):
tag="waiilabs/sandbox:aarch64-latest"
Run the docker container with your configured LLM provider. See Configuring LLM Providers for detailed instructions on setting up your preferred provider (OpenAI, Azure OpenAI, AWS Bedrock, etc.).
docker run -i -t --rm \
--env OPENAI_API_KEY=$OPENAI_API_KEY \
-p=3000:3456 \
-p=9859:9859 \
-v `<abs-path-to>`/waii-sandbox-test/pg:/var/lib/postgresql/data:rw \
-v `<abs-path-to>`/waii-sandbox-test/log:/tmp/logs:rw \
--platform linux/amd64 \
--name waii $tag --debug
The above command does the following:
- Injects the OpenAI key as an environment variable: Ensures the container has access to the OpenAI API for LLM interactions.
- Maps ports: Maps port 3000 and 9859 from the host to the container, allowing external access to these services.
- Binds two volumes:
- One for PostgreSQL data: Ensures database persistence across container restarts.
- Another for logs: Facilitates logging and troubleshooting.
- Removes the container once it stops: Cleans up resources by removing the container automatically after it's stopped, preventing unnecessary storage usage.
The above command does the following:
- Injects the openai key as an environment variable
- Maps port 3000 and 9859 from the host to the container.
- Binds two volumes: one for PostgreSQL data and another for logs.
- Removes the container once it stops.
Run the Waii container with Azure OpenAI / Bedrock, etc.
# the rest of the command is same as before, you only need to add this line, and remove --env OPENAI_API_KEY
tag="waiilabs/sandbox:latest"
docker run -i -t --rm \
-v `<absolute-path-to-azure_openai_endpoint.yaml>`:/waii/llm_endpoint.config \
# If you are using <= 1.27.x, you need to specify the models.config file, but >= 1.28.x, you don't need to specify the models.config file
-v `<absolute-path-to-azure_openai_models.yaml>`:/waii/models.config \
-p=3000:3456 \
-p=9859:9859 \
-v `<abs-path-to>`/waii-sandbox-test/pg:/var/lib/postgresql/data:rw \
-v `<abs-path-to>`/waii-sandbox-test/log:/tmp/logs:rw \
--platform linux/amd64 \
--name waii $tag --debug
Run the Waii container with external RDS
By default, the Waii container will use the embedded PostgreSQL database within the container. If you want to use an external RDS database, you can specify the following environment variable when you start the Docker container:
IMPORTANT: You should use one RDS database for one Waii instance. (You can still use the same RDS instance, but you should create a new database for each Waii instance.)
docker run <other-options> \
--env RDS_URL="postgresql://username:password@password:5432/db_for_waii_to_use"
$tag ...
You can follow the doc Setup Postgres database for self-hosted Waii to setup a Postgres database.
Access the waii UI:
Open your browser and navigate to: http://localhost:3000.
By default, the WAII dataset is pre-loaded into the system, allowing you to begin exploring the tool immediately.
Running CLI commands:
To generate a query, run:
waii query create "which airlines offer the largest number of destinations? List top three, include their names, country and number of destinations."
Using Waii API
You can also use Waii API, such as https://github.com/waii-ai/waii-sdk-py (Python), https://github.com/waii-ai/waii-sdk-js (Javascript) to talk to the Docker sandbox service.
For Javascript, you need to initialize the WAII client by specifying the URL to your local Docker container:
// Import the WAII module
import WAII from 'waii-sdk-js';
// Initialize WAII with the URL and API key
WAII.initialize('http://localhost:9859/api/', '');
Similarily, for Python:
from waii_sdk_py import WAII
from waii_sdk_py.query import *
WAII.initialize(url='http://localhost:9859/api/')
Setting Up Your Own Database
To make waii work with your own Snowflake database, follow the steps outlined below. This will allow waii to index and use your database.
Access the waii UI:
Navigate to the waii user interface by opening your browser and going to:
http://localhost:3000
Add a new database connection:
Please refer to the Adding a Database Connection documentation for detailed instructions on how to add a new database connection.
Security settings
By default Waii Docker container runs in non-secure mode, which means anyone can access the UI and API endpoints.
Following are the security settings you can use to secure the Waii Docker container:
Enable simple username/password the UI (Not for API)
You can specify the following environment variable to secure the UI (only)
Specify --env SIMPLE_PASSWORD=true when you start the Docker container. This will prompt you to set a password for the UI.
The username/password please ask Waii team for the default username/password.
Important: if you enable API key auth (below), you don't need to enable simple password auth.
Enable API key authentication for the API and UI
If you want to secure the API and UI with an API key, you can specify the following environment variable when you start the Docker container:
docker run ... --env WAII_DEFAULT_API_KEY=abc123 ... waiilabs/sandbox:<tag> --api_key_auth_enabled
(1) (2)
Comparing to regular command, you need to specify (1) and (2) to enable API key authentication.
You can specify any API key you want to use, for example, abc123. You can then use this API key to access the API and UI.
Once the API key is set, you can access the UI by navigating to top-right hamburger menu -> API key sign-in -> enter abc123.
The same API key can be used to access the API endpoints. For example if you are using Python SDK, you can specify the API key in the initialize function:
WAII.initialize(url='...', api_key="abc123")
Or curl:
curl 'http://localhost:9859/api/update-db-connect-info' \
-H 'Authorization: Bearer abc123' \
-H 'Content-Type: application/json' \
--data-raw '{"scope":""}'
Enable output streaming to stdout
| Environment Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
REDIRECT_LOGS_DOCKER | Redirect all container logs to stdout after commands complete | false |
ENABLE_LOG_STREAMING_DOCKER | Stream docker command output to stdout in real-time | false |
These are all environment variables, you should use --env when you start the Docker container. (before the image name)
e.g.
docker run -i -t --rm \
--env REDIRECT_LOGS_DOCKER=true \
...
waiilabs/sandbox...
Other config options
(Note: these are NOT environment variables, but config options, you should use --conf AFTER the image name)
You can specify the following config options to customize the behavior of the Waii Docker container:
| Variable | Description | Default |
|---|---|---|
ENABLE_SHARED_CONNECTIONS | Allows shared database connections between users. If multiple users (e.g. user1@postgres1 and user2@postgres1) have access to the same tables, indexing only happens once as both users can access the same index. | false |
LARGE_TRINO_ICEBERG_CATALOG | For Trino only. Set to true to improve performance when using Trino with large Iceberg catalogs. | false |
You can specify them using --conf CONFIG_VAR=VALUE when you start the Docker container, multiple options can be specified by repeating the option, e.g. --conf ENABLE_SHARED_CONNECTIONS=true --conf LARGE_TRINO_ICEBERG_CATALOG=true.
Example:
docker run -i -t --rm \
--env OPENAI_API_KEY=$OPENAI_API_KEY \
-p=3000:3456 \
-p=9859:9859 \
waiilabs/sandbox... --conf ENABLE_SHARED_CONNECTIONS=true --conf LARGE_TRINO_ICEBERG_CATALOG=true
Conclusion
You have successfully deployed a single node instance of Waii on Docker!